Heat

It’s hot – and it’s getting hotter. Climate change is increasing the number of extreme-heat days across the US. This increase in heat is dangerous for outdoor workers, from agricultural workers, to roofers and construction workers, to airport runway workers. It’s also concerning for certain indoor workers who do not have a climate-controlled environment, like some workers in restaurants, packing houses, and warehouses.
Agricultural workers are particularly vulnerable to overexertion in the heat. Piecework pay (rather than hourly wages) discourages the utilization of break times during which they could rehydrate and rest in the shade. Agricultural workers on large farms may find shade and water break locations far from their working location. Some who apply pesticides may need to wear personal protective equipment which increases the risk of heat stress. Concurrent exposures to wildfire smoke, now a regular occurrence in summers and falls across the West, or to pesticides, may exacerbate underlying health conditions that are already triggered by heat stress, like asthma. Further, many may leave a hot workplace at the end of the day to return to substandard farm housing without climate controls and with insufficient ventilation, reducing their bodies’ ability to recover during the night.
There are currently no federal heat regulations, meaning workers are not legally protected from working in dangerously hot conditions or ensured basic safety precautions are followed. Several states have standards: California, Washington, Oregon, Colorado, Minnesota, and Maryland. California’s standard, for example, requires the provision of rest, shade, and water – the three critical aspects to prevent heat-related illnesses and to alleviate mild heat-related illnesses. Around the country, however, many workers are unaware of the health risks of extreme heat, nor the increased risks of heat-related illness as a result of climate change.
|
MCN Heat Resources and Webinars |
Heat-Related Illness Clinician’s Guide
English | Spanish
This guide, developed by MCN and Farmworker Justice, provides clinical information on the prevention and treatment of heat-related illness. Since workers may not be familiar with the signs of heat stress, it is important that clinicians discuss symptoms and prevention with farmworkers and others at risk of heat-related illness.
Heat-related Illness and Farmworkers: Bilingual Training Curriculum & Facilitator Guide
This comprehensive training curriculum in Spanish or English is designed as a practical resource to train farmworker about heat-related illness including signs and symptoms, how to prevent it, and what to do when someone is experiencing heat-related illness.

Webinar Series: Just Play It Cool - Community Health Center Resources to Address Heat and Climate Change
English | Spanish

Webinar: It's Hot and It's Dangerous!
English | Spanish
A webinar for community health workers to learn about heat-related illness and how to prevent it.
|
Resources |
||||||||
Fired Up! Workers for Heat Justice - National COSH's Worker for Heat Justice page |
||||||||
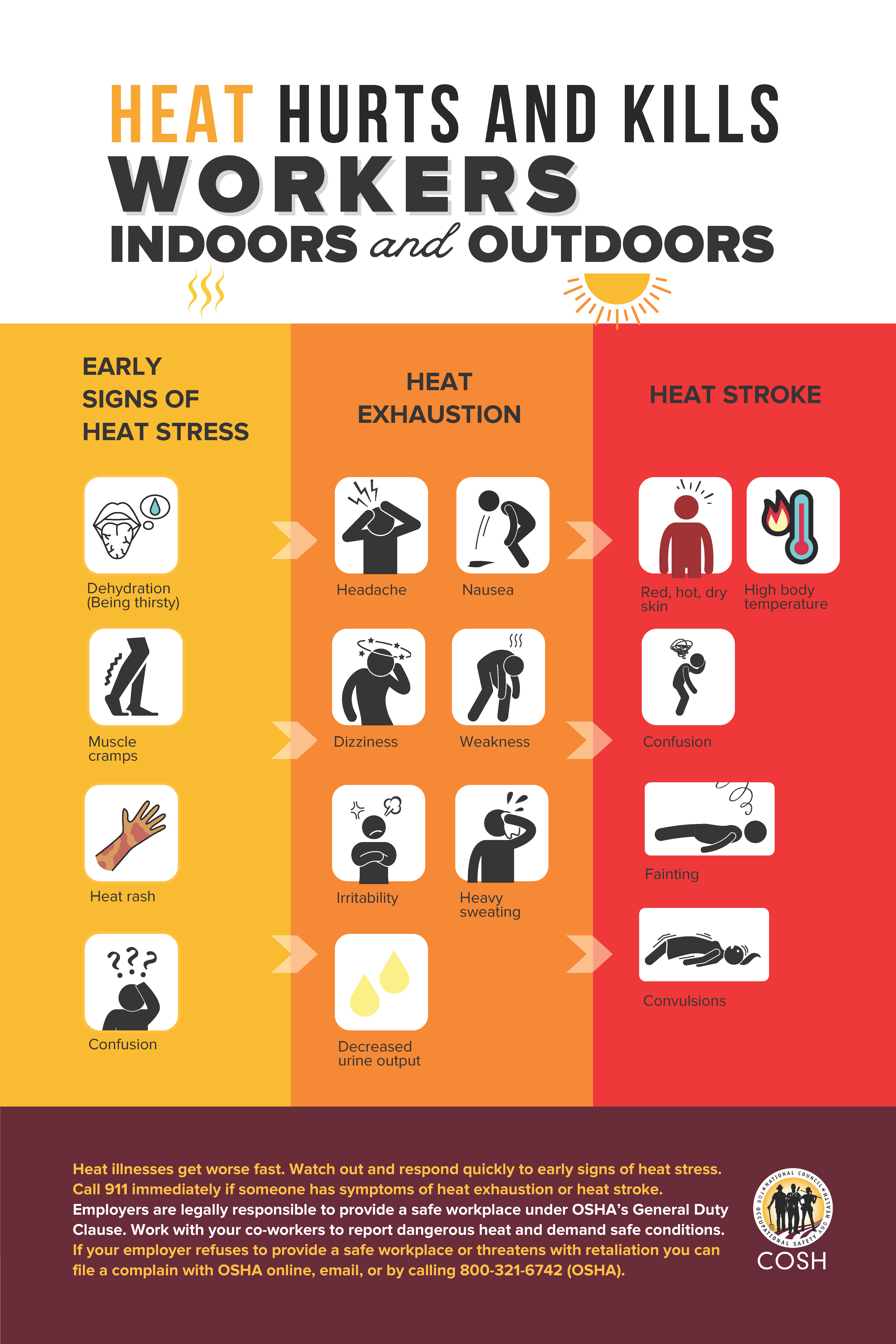
California Heat Illness PreventionThis page overviews the CA Heat Illness standard and resources in multiple languages. |
OSHA Heat Safety Tool AppCalculates the heat index for their worksite, and, based on the heat index, displays a risk level to outdoor workers. |
|||||||
|
||||||||
|
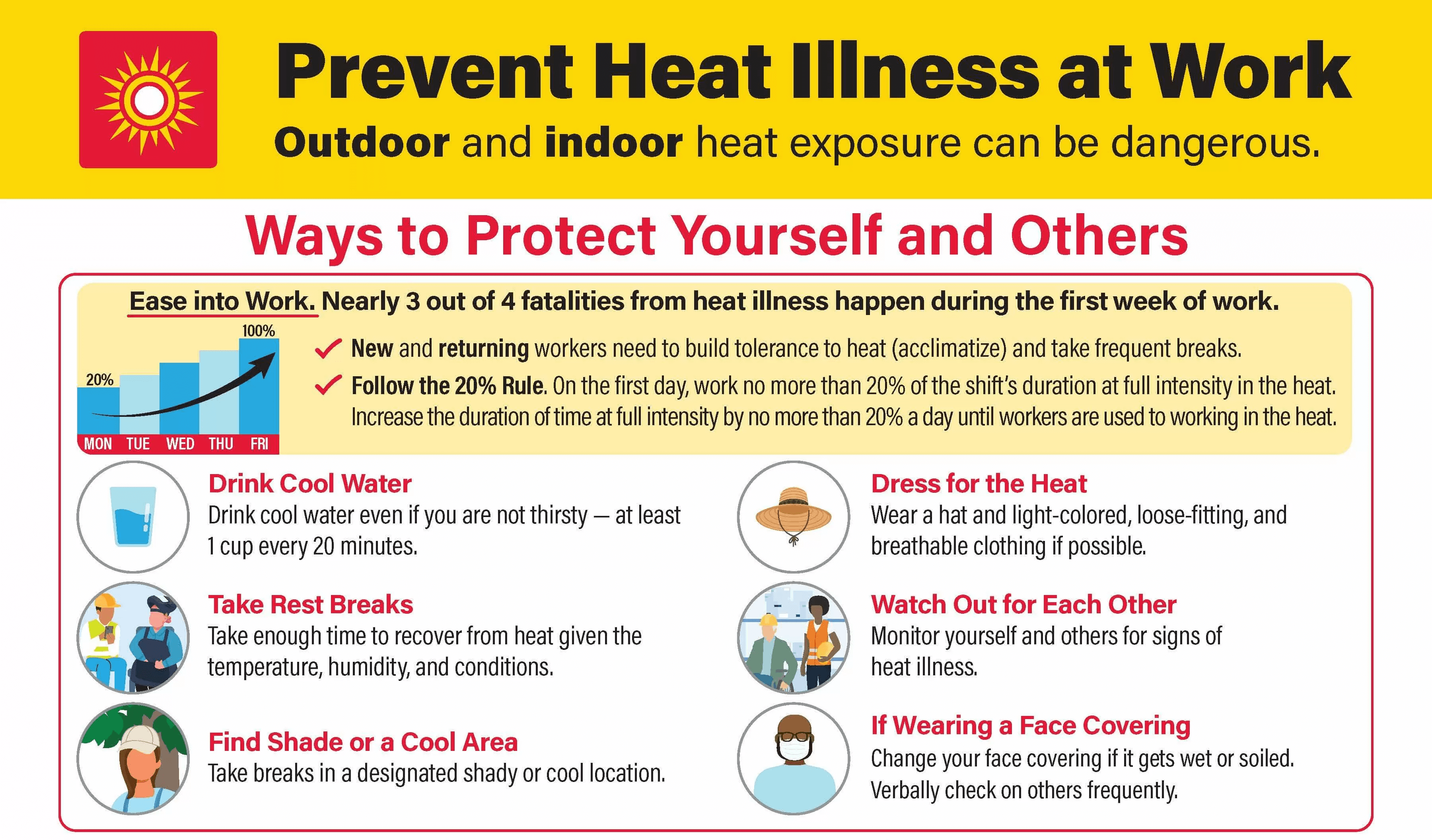
OSHA: Prevent Heat Illness at WorkEnglish | SpanishA simple guide for heat-related illness prevention and first aid for workers. |
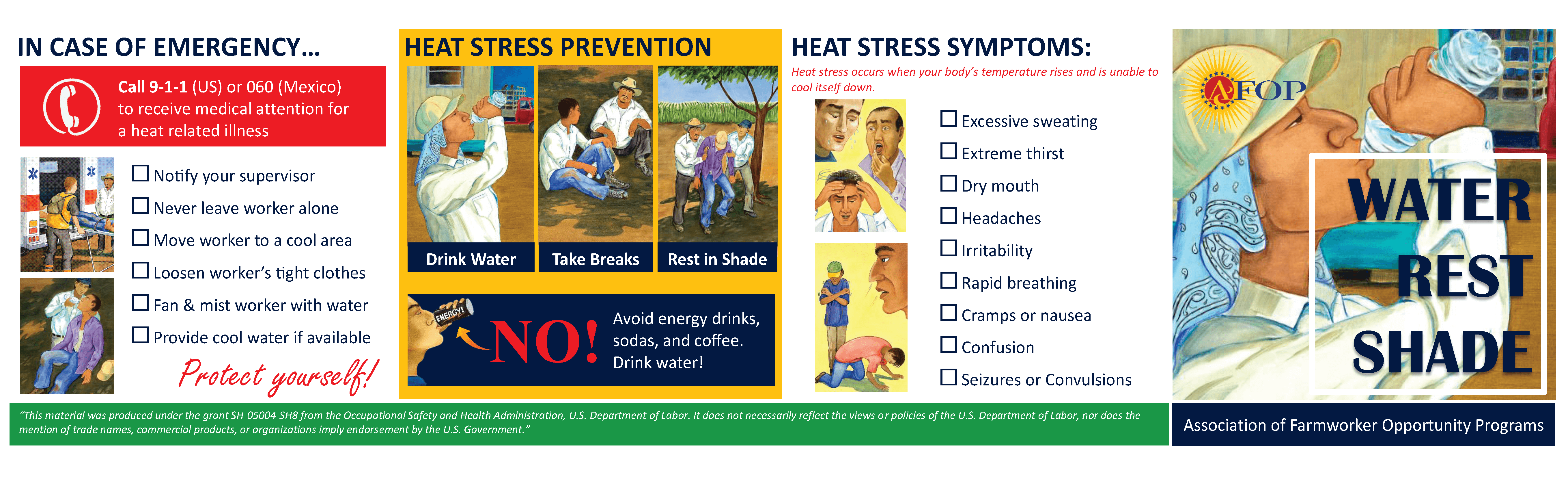
Water, Rest, Shade Fact SheetEnglish | Spanish |
|||||||
|
|
||||||||
PNASH Heat Illness Prevention ToolkitA set of resources and tools developed in collaboration with agricultural workers and educators. The toolkit provides a train-the-trainer guide for the identification, prevention, and treatment of heat illness. Available in English and Spanish. |
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
|
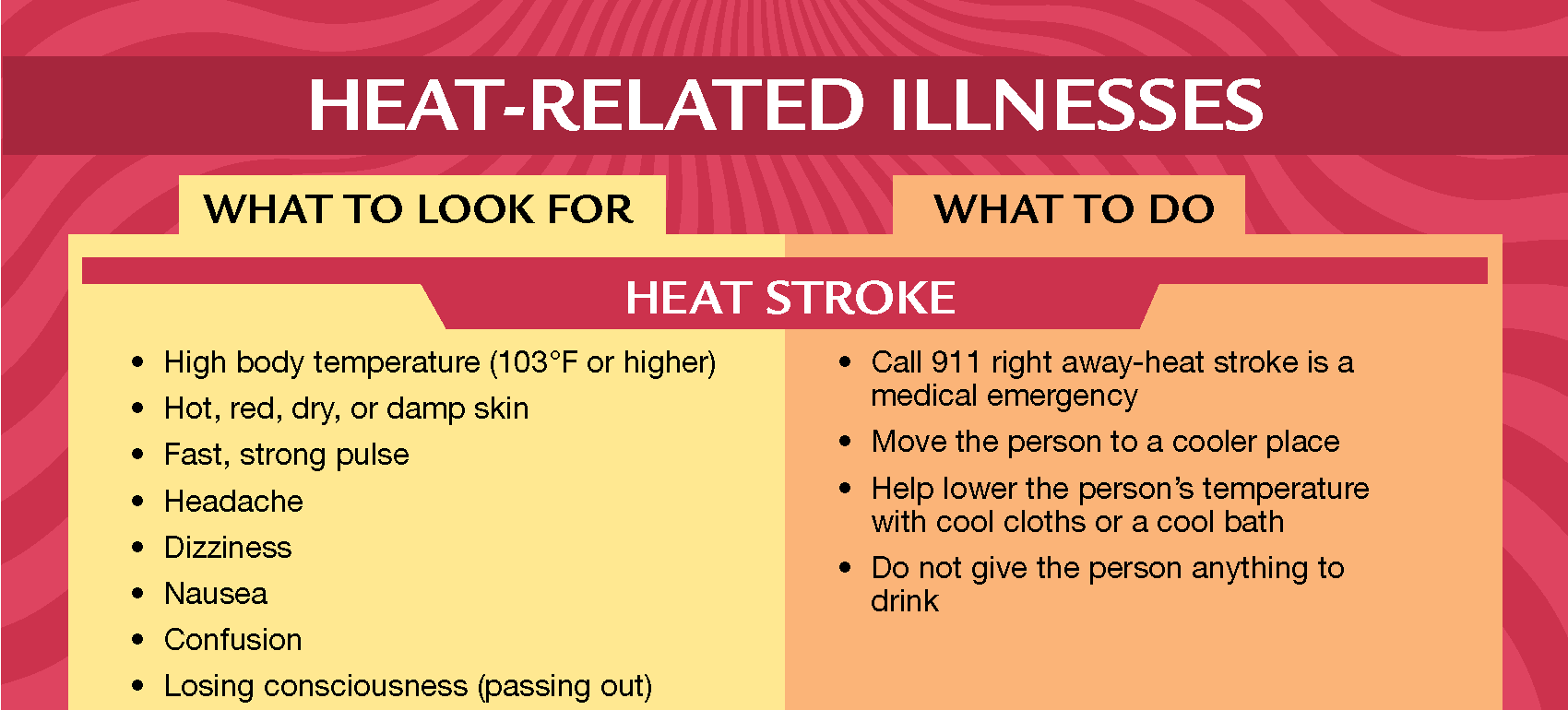
Heat-Related Illnesses - What to Look For / What to DoEnglish | Spanish |
|||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
|
Heat Illness Prevention |
|||||||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Advocacy and Media |
-
Health Secretary Becerra touts extreme heat protections. Farmworkers want more
-
‘It Smells Bad’: The US Farmworkers Grappling with Unsafe Water at Home
-
Climate Change is Impacting Health Care Provision. Community Health Centers Push Back
-
Why Respiratory Risks like Smoke Hit Low-Income Workers the Hardest
-
Can Health Centers Affect Climate Change? A Review of the Landscape, and Call to Action
-
Supervisor Believed Construction Worker Was on Drugs. He Was Dying of Heat Stress.